Having the right size nut is crucial for any successful fastening project. Nuts that are too small won’t provide enough grip, while oversized ones might not fit through the designated hole or strip the threads. In the UK, nuts (and bolts) follow the metric system, so understanding how to measure them in millimeters (mm) is essential for DIY enthusiasts and professionals alike.
This guide will walk you through the process of measuring nut size, explain the metric system for nuts, and offer some helpful tips to ensure you get the perfect fit every time.
Tools Required for Measuring Nut Size
Calipers
Calipers are precision tools used to measure the external and internal dimensions of objects. There are three main types:
- Digital Calipers: These provide a digital readout, making them user-friendly and highly accurate.
- Dial Calipers: These feature a dial gauge for reading measurements, offering good accuracy.
- Vernier Calipers: These are the traditional type, requiring manual reading of scales but are very precise.
Ruler or Tape Measure
A ruler or tape measure is a basic tool that can be used for quick measurements. It’s less precise than calipers but can be sufficient for larger nuts or when exact precision is not critical.
Thread Gauge
A thread gauge is used to measure the pitch or number of threads per inch (TPI) on a nut or bolt. This tool is essential for ensuring that the nut fits correctly onto the bolt.
Nut Size Charts
Nut size charts provide a reference for standard nut sizes and their corresponding measurements. These charts are widely available online and in hardware stores, making them a handy tool for identifying nut sizes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Measuring Nut Size
Measuring the Diameter
- Using Calipers:
- Open the calipers and place them across the widest part of the nut.
- Ensure the calipers are perpendicular to the nut for an accurate measurement.
- Read the measurement on the digital display, dial, or vernier scale.
- Using a Ruler or Tape Measure:
- Place the ruler or tape measure across the nut’s widest part.
- Read the measurement to the nearest millimeter or inch.
- This method is less precise but useful for a quick reference.
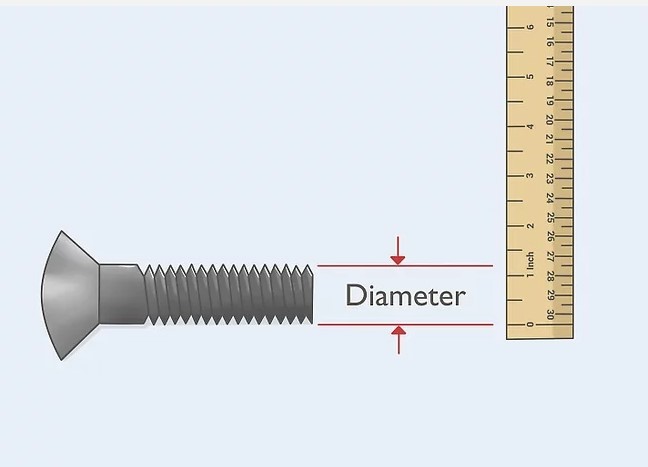
Image source: wikihow
Measuring the Thread Pitch
- Understanding Thread Pitch:
- Thread pitch is the distance between threads, measured in millimeters for metric nuts or as the number of threads per inch (TPI) for imperial nuts.
- Using a Thread Gauge:
- Select the appropriate gauge for either metric or imperial threads.
- Match the gauge teeth with the nut threads until you find a perfect fit.
- Read the measurement directly from the gauge.
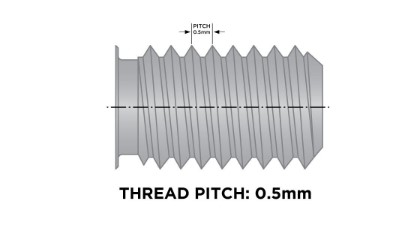
Image source: huyett
Identifying the Nut Type
Different types of nuts include hex, square, wing, and more. Identifying the type is crucial as it influences the measurement process and application.
- Hex Nuts: The most common type, typically measured across the flats (the distance between opposite sides).
- Square Nuts: Measured in a similar way to hex nuts, but with four sides.
- Wing Nuts: These have “wings” for manual tightening and are measured across the wings.

Image source: skillcatapp
Converting Measurements
Metric to Imperial Conversion
Metric sizes are converted to imperial by dividing the millimeter measurement by 25.4 (since 1 inch = 25.4 mm). For example, a 10 mm nut is approximately 0.394 inches.
Imperial to Metric Conversion
Imperial sizes are converted to metric by multiplying the inch measurement by 25.4. For instance, a 1/2 inch nut is approximately 12.7 mm.
Using Nut Size Charts
Reading a Nut Size Chart
Nut size charts list standard nut sizes along with their corresponding diameters and thread pitches. Here’s how to use them:
- Find the diameter measurement on the chart.
- Locate the corresponding thread pitch.
- Identify the standard size notation (e.g., M10 for metric or 1/2”-13 for imperial).
Common Nut Sizes in the UK
- Metric Sizes: Common sizes include M4, M6, M8, M10, and M12, where “M” denotes metric and the number indicates the diameter in millimeters.
- Imperial Sizes: Common sizes include 1/4”-20, 3/8”-16, and 1/2”-13, where the first number is the diameter in inches and the second is the TPI.
Tips for Accurate Measurement
Ensuring Precision
- Calibration of Tools: Regularly calibrate your calipers and thread gauges to maintain accuracy.
- Measuring at the Widest Points: Always measure at the nut’s widest points to ensure consistency.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Misreading Measurements: Double-check your readings, especially with vernier calipers.
- Overlooking Thread Pitch: Always measure and confirm the thread pitch to avoid mismatched nuts and bolts.
Practical Applications
DIY Projects
In DIY projects, accurate nut measurement is critical for assembling furniture, installing fixtures, and other tasks. Incorrect measurements can lead to loose fittings or structural issues.
Automotive Repairs
In automotive repairs, using the correct nut size is vital for safety and performance. From securing engine components to fitting wheels, precision ensures reliability.
Construction and Engineering
In construction and engineering, accurate nut measurement ensures structural integrity and compliance with specifications. Missteps here can lead to safety hazards and costly reworks.
Troubleshooting
What to Do if Measurements Don’t Match
- Re-measure: Take multiple measurements to ensure consistency.
- Double-check Tools and Charts: Verify that your tools are calibrated and that you are referencing the correct chart.
Finding Uncommon Nut Sizes
- Where to Look: Specialized hardware stores and online retailers often stock uncommon sizes.
- Custom Ordering: For rare sizes, consider custom manufacturing or ordering from specialty suppliers.
Conclusion
Measuring nut size accurately is essential for any DIY, automotive, or engineering project. In the UK, understanding both metric and imperial measurement systems ensures you select the right nut for your needs. Utilize tools like calipers, rulers, and thread gauges, and consult nut size charts for precision.
Always measure the diameter and thread pitch carefully, and convert measurements when necessary. Accurate nut measurements lead to better project outcomes, enhancing both safety and functionality. For further details, explore our comprehensive guide and resources on measuring nut size in the UK.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To determine the size of a nut, measure the diameter of the nut’s internal thread using calipers or a ruler. Additionally, measure the thread pitch with a thread gauge. Cross-reference these measurements with a nut size chart to identify the standard size.
An M10 bolt is a metric bolt with a nominal diameter of 10 millimeters. The “M” stands for metric, and the number “10” indicates the bolt’s diameter.
An M12 nut is designed to fit an M12 bolt, which has a nominal diameter of 12 millimeters. The nut itself typically has an external width (across flats) of about 18 millimeters.
A 13mm nut typically fits an M8 bolt, meaning the nut is designed for a bolt with an 8 millimeter diameter. The “13mm” refers to the nut’s external width across the flats.
